
CEPROTIN (human protein c): Clinical Data & Safety information
Study Design:1
A prospective, multicentre, open-label, phase 2/3 study was conducted to demonstrate the safety profile and efficacy of CEPROTIN® for the treatment of purpura fulminans (PF) and acute thromboembolic events.
Eighteen patients with severe congenital protein C deficiency (SCPCD) were enrolled (ages ranging from newborn to 26 [rounded to nearest year]), with 15 receiving CEPROTIN®.
The primary efficacy endpoint of the study was to assess whether episodes of PF and/or other thromboembolic events were treated effectively, effectively with complications, or not treated effectively, compared with historical control data. Safety assessments included adverse events and proportion of patients who developed inhibitors to protein C (PC).
94.7% of CEPROTIN® treatments (N=19) were rated as effective compared to 52.2% of the historical controls1
Effective:1
The final treatment modality was effective and the patient was discharged on a stable anti-coagulation regimen
Ineffective treatment modalities were disregarded, because in the historical control they could have been applied before the proper diagnosis of protein C (PC) deficiency was available (e.g. antibiotics for presumed sepsis)
Effective with complications:1
The final treatment modality was effective (possibly with complications) and
The patient was discharged on a stable anti-coagulation regimen, but ≥1 treatment modality was effective with complications
Not effective:1
The final treatment modality was ineffective and/or
The patient was not discharged on a stable anti-coagulation regimen
The primary efficacy rating was taken from 18 episodes of PF treated with CEPROTIN® compared to 21 episodes of PF in the historical control group.
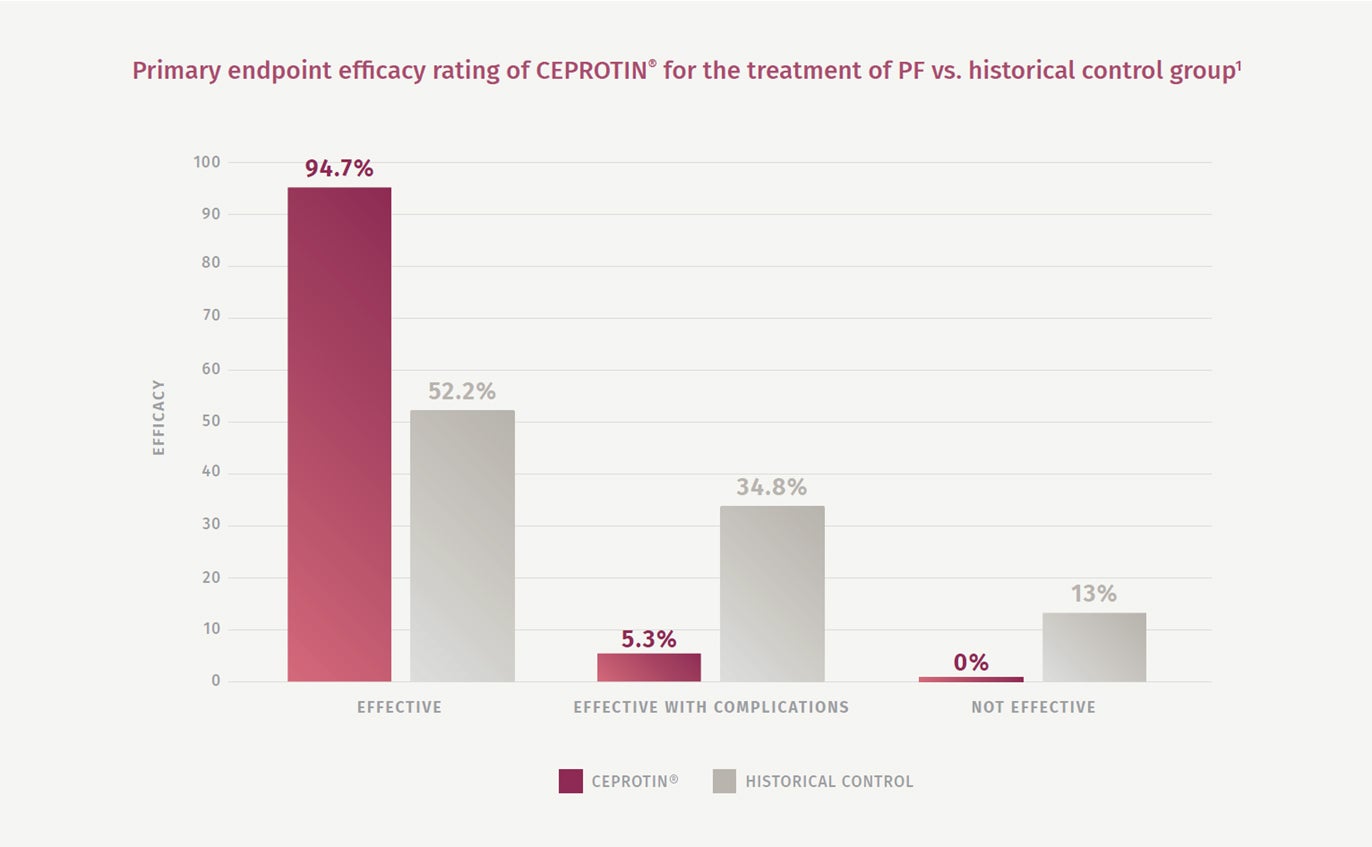
A significant therapeutic benefit was demonstrated in patients treated with CEPROTIN®, with a 94.7% complication-free treatment rate vs. the historical control group treated with conventional therapy (52.2%)1
The number of PF episodes deemed as ‘effective with complications’ was 5.3% with CEPROTIN® vs. 34.8% with historical controls1
Safety profile results:1
Of the 15 patients treated with CEPROTIN® in the study, nine (60%) experienced serious adverse events, and all 15 experienced non-serious adverse events; all adverse events were considered by investigators to be unrelated to CEPROTIN®
There were no bleeding complications associated with CEPROTIN® therapy
No adverse events resulted in study withdrawal
No protein C inhibitory antibodies were detected throughout the study

Excellent:1
No new skin lesions after 48 h of treatment and
Complete resolution* of non-necrotic skin lesions by day 5 of treatment with no further progression while on protein C concentrate until successful establishment of adequate anticoagulation† and
Resolution‡ of necrotic lesions by day 14 (± 2) of treatment
Good: 1
No new skin lesions after 48 h of treatment and
Complete resolution of non-necrotic skin lesions between day 6–14 of treatment with no further progression while on protein C concentrate until successful establishment of adequate anticoagulation; and
Resolution of necrotic lesions between day 14 (± 2) and day 28 (± 2) of treatment
Fair: 1
No new skin lesions after 48 h of treatment and
Complete resolution of non-necrotic skin lesions after more than 14 (± 2) days of treatment with no further progression while on protein C concentrate until successful establishment of adequate anticoagulation; and
Resolution of necrotic lesions after >28 (± 2) days of treatment
* Definition of complete resolution of non-necrotic lesion: no infarcted skin, no indurations and pain. 1
† Oral anticoagulation did not have to be achieved if the patient is transitioning to Part 2 (short-term prophylaxis with protein C concentrate) or Part 3 (long-term prophylaxis with protein C concentrate). 1
‡ Definition of resolution of necrotic lesion: lesion completely covered by clean granulation tissue or tissue is successfully engrafted. 1
Prophylaxis and other clinical studies
Twelve courses of short-term prophylaxis prior to surgery or invasive therapy and 7 courses of long-term prophylaxis were included in the efficacy analyses for CEPROTIN®.2
No formal clinical study in either paediatric or neonatal population with severe congenital protein C deficiency was ever conducted. However, several small retrospective and prospective studies investigating other clinical application areas have been published in this population. Indication was prevention and treatment of purpura fulminans and thrombotic disease, enrolling overall 14 subjects of 2 days old throughout adolescence. 2
A retrospective surveillance program observed more than 10 years of CEPROTIN® use on 79 patients with protein C deficiency of different origins, treated for acute episodes, short-term and long-term prophylaxis, confirming efficacy and safety profile.3
Special warnings and precautions for use
For full safety and special warnings and precautions please refer to the SmPC 2
CEPROTIN® is indicated for prophylaxis and treatment of purpura fulminans coumarin-induced skin necrosis and venous thrombotic events in patients with severe congenital protein C deficiency.2
-
Manco-Johnson MJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of protein C concentrate to treat purpura fulminans and thromboembolic events in severe congenital protein C deficiency. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116:56–68.
-
CEPROTIN® 500 IU Summary of Product Characteristics.
-
Knoebl PN. Severe congenital protein C deficiency: the use of protein C concentrates (human) as replacement therapy for life-threatening blood-clotting complications. Biologics: Targets & Therapy. 2008;2(2):285–96.


